With technology advancing at breakneck speed, big data has stepped up from simple storage to a crucial tool in strategic decision-making across multiple sectors. This is especially true in seismic data analytics, where the immense volume of geophysical data is tapped to unveil significant economic opportunities.
Seismic data analytics, a specialized segment of big data, involves interpreting and manipulating massive datasets collected through geological surveys, primarily used to identify and quantify subsurface structures. The financial implications of this data are profound, offering oil exploration to environmental management industries a pathway to enhance operational efficiency and innovate in cost-saving and resource allocation strategies.
![]()
Scope of Seismic Data & Challenges
Seismic data encompasses high-resolution images generated by sound waves, which help map the Earth’s subsurface structures. Companies in the oil and gas sector, for instance, rely on this data to pinpoint potential drilling sites and assess reservoir viability, a practice that significantly reduces the risks associated with exploration and drilling.
The primary challenges of seismic data analytics stem from its three Vs:
- Volume: The sheer amount of data generated can be overwhelming.
- Velocity: The speed at which new data is generated and needs to be processed.
- Variety: Data comes in various formats, which complicates aggregation and analysis.
Optimizing Operational Outcomes with Artificial Intelligence
Seismic data analytics enhances drilling accuracy, significantly reducing the likelihood of unproductive wells. This precision leads to substantial cost reductions and accelerates decision-making processes, giving companies a competitive edge. Integrating artificial intelligence into seismic imaging allows for high-resolution, accurate 3D models even under constraints, enhancing reservoir modeling and production planning.
Additionally, the integration of seismic AI through machine learning algorithms improves the analysis of seismic data. This results in more precise predictions of subsurface conditions, improving exploration and production success rates while minimizing environmental impacts. These improvements demonstrate how technological AI advancements are reshaping industry standards and operational efficiencies.
While seismic data analytics offers numerous benefits, it is not without its risks. The high cost of data collection and the potential for technological failure pose significant challenges. Moreover, relying on sophisticated AI models requires constant updates and maintenance to ensure accuracy.
In a practical application of these advancements, Eliis and Chevron have partnered to advance AI in seismic interpretation, boosting the speed and accuracy of subsurface modeling, which is crucial for carbon sequestration projects. Their collaboration has developed AI algorithms that streamline seismic data analysis, enabling quicker, more detailed geological model creation and improving the assessment of storage site integrity. This case clearly shows how integrating AI can transform traditional practices in the energy sector and lead to significant gains in efficiency and accuracy.
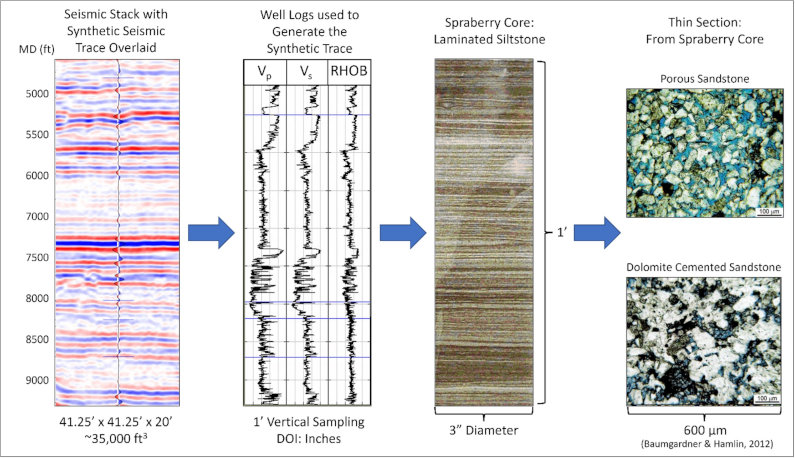
Strategic Recommendations for Seismic Data Utilization
For small businesses and startups in the geosciences sector, the following strategies can ensure the effective utilization of seismic data analytics:
Invest in Robust Analytics Tools
Identify and deploy cutting-edge analytical software specializing in seismic data. Such tools can handle complex computations and large datasets more efficiently than generic software, offering faster insights and better scalability. Startups should look for customizable platforms that can grow with their needs, ensuring they can continue to manage increasing amounts of data without performance bottlenecks.
Prioritize Data Quality
High-quality data is paramount for accurate analysis. Businesses should develop rigorous data collection and management protocols to ensure accurate, complete, and timely data. This might involve regular audits, using high-quality sensors, and training personnel in best data practices. Ensuring data integrity from the outset reduces costly errors in analysis and helps in building models that truly reflect subsurface realities.
Foster Collaboration
Collaborate with technology leaders and industry innovators to gain access to advanced tools and methodologies. Partnerships can also extend to academic institutions where cutting-edge geophysics and data science research is often conducted. By collaborating, small businesses can tap into a larger knowledge base, share risks, and reduce costs associated with R&D.
Stay Updated
The field of seismic AI is rapidly evolving. Companies must stay informed about the latest technological advancements and industry trends. Attending industry conferences, subscribing to relevant publications, and participating in professional networks can help businesses stay at the forefront of technology. This ongoing learning will enable them to make informed decisions about when to adopt new technologies or approaches.
Implement Data Governance
Establish a strong data governance framework that outlines policies and procedures for data handling, storage, and analysis. This framework should address data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance, particularly as data breaches and cyber threats become more prevalent. A well-defined data governance policy helps build trust with stakeholders and ensures that the data’s integrity is maintained throughout its lifecycle.
The strategic use of seismic data analytics signifies a transformative approach in various industries, offering a blend of enhanced accuracy, cost efficiency, and faster decision-making. By adopting a balanced approach that includes investment in technology and continuous improvement of data quality, companies can maximize the financial potential offered by this dynamic field.

